Anatomy and physiology are foundational sciences studying the structure and function of the human body. Anatomy focuses on physical structures, while physiology explores their functions; Together, they provide a comprehensive understanding of how the body operates, essential for healthcare and biological sciences. These disciplines are deeply interconnected, forming the basis for medical practice, research, and education. Understanding anatomy and physiology is crucial for diagnosing diseases, developing treatments, and appreciating human health and wellness. They also serve as the cornerstone for advanced studies in specialized fields like neurology, cardiology, and orthopedics. Effective study of these subjects requires a combination of theoretical knowledge, practical observation, and clinical application.
1.1 Definition and Scope
Anatomy is the scientific study of the structure and organization of body parts, focusing on their physical relationships. Physiology examines the functions and processes that enable the body to operate, from cellular activities to systemic interactions. Together, they form the cornerstone of understanding human health and disease. The scope of anatomy includes gross, microscopic, and developmental studies, while physiology encompasses systemic, cellular, and molecular functions. These disciplines are essential for medical education, research, and clinical practice, offering insights into the body’s intricate mechanisms.
1.2 Importance of Studying Anatomy and Physiology
Studying anatomy and physiology is crucial for understanding the human body’s structure and function. It forms the foundation for careers in healthcare, enabling professionals to diagnose and treat conditions effectively. Anatomy provides a vocabulary for medical communication, while physiology explains how the body responds to health and disease. These sciences also underpin advancements in medical research, therapy development, and patient care. They empower individuals to appreciate health, prevent diseases, and make informed decisions about their well-being. This knowledge is vital for both personal and professional applications.
Branches of Anatomy
Anatomy is divided into three primary branches: Gross Anatomy, Histology, and Cytology. Gross Anatomy studies large body structures, while Histology focuses on tissues and Cytology on cells.
2.1 Gross Anatomy
Gross Anatomy focuses on the study of large body structures visible to the naked eye, such as organs and bones. It examines the physical organization of the body and how different parts are interconnected. This branch is crucial for understanding the spatial relationships between body components. Gross Anatomy is subdivided into regional and systemic approaches. Regional Anatomy studies specific body regions, while systemic Anatomy explores systems like the circulatory or nervous system. It is essential for medical professionals and students to grasp foundational knowledge of human structure through dissection and imaging techniques. Gross Anatomy provides a macroscopic perspective, complementing microscopic studies and aiding in clinical diagnostics and surgical practices. It forms the basis for advanced anatomical and physiological understanding in healthcare fields.
2.2 Histology
Histology is the microscopic study of tissues, examining their cellular structure and organization. It focuses on how cells group together to form tissues, which perform specialized functions. Histology is essential for understanding tissue development, repair, and disease mechanisms. By studying tissue samples under a microscope, histologists can identify normal and pathological conditions. This knowledge aids in diagnosis and treatment of diseases, linking microscopic observations to macroscopic anatomical and physiological processes. Histology complements gross anatomy by providing detailed insights into tissue composition and function. It is a critical tool in medical research and education, enhancing understanding of human health and disease.
2.3 Cytology
Cytology is the study of cells, focusing on their structure, function, and behavior. It examines cellular components like the nucleus, mitochondria, and organelles, providing insights into how cells operate. Cytology is crucial for understanding cellular processes, such as division, metabolism, and signaling. It aids in diagnosing diseases by identifying abnormal cell changes, like cancer. This field bridges anatomy and physiology by linking microscopic cellular functions to overall body systems. Cytology is essential in medical diagnostics and research, advancing our understanding of health and disease. It is a fundamental area of study in biology and medicine, offering detailed perspectives on cellular life. By analyzing cells, cytology contributes to personalized medicine and therapeutic advancements. This knowledge is vital for developing targeted treatments and understanding human physiology at its most basic level. Cytology’s applications span from routine health screenings to cutting-edge scientific research, making it indispensable in modern healthcare and education.
Branches of Physiology
Physiology branches include systemic and specialized fields. Systemic studies specific systems like the nervous or circulatory, while specialized focuses on processes like neurophysiology or cellular function, aiding understanding of bodily functions and adaptations.
3;1 Systemic Physiology
Systemic physiology focuses on the functions of specific body systems, such as the nervous, circulatory, and respiratory systems. It examines how each system operates individually and contributes to overall bodily functions. For example, the nervous system controls communication through neurons, while the circulatory system transports oxygen and nutrients. This branch provides a detailed understanding of how systems interact to maintain health and enables the diagnosis of disorders. Studying systemic physiology is crucial for advancing medical treatments and therapies.
3.2 Specialized Physiology
Specialized physiology delves into specific, intricate functions within organisms, often focusing on particular tissues, organs, or systems. It explores advanced topics like neurophysiology, endocrinology, and cardiology, examining how specialized cells and systems regulate bodily processes. This branch emphasizes the study of unique functional adaptations, such as nerve impulse transmission or hormonal regulation. Specialized physiology integrates with fields like genetics and biochemistry to uncover mechanisms underlying complex physiological processes, aiding in the development of targeted medical treatments and therapies for specific conditions.
Key Concepts in Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy and physiology revolve around understanding the body’s structural organization and functional systems. Key concepts include levels of organization, from cells to systems, and how they interact. The relationship between structure and function is central, explaining how body parts operate cohesively. These principles form the foundation for understanding human health, enabling the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. Mastery of these concepts is essential for advancements in medical science and practice.
4.1 Levels of Structural Organization
The human body is organized into six structural levels: cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and the organism. Cells are the basic units, forming tissues that specialize into functions. Tissues combine to create organs, which perform specific roles. Organs work together in systems like the nervous or circulatory, contributing to the body’s overall function. This hierarchical organization ensures efficiency and complexity, allowing the body to maintain homeostasis and respond to environmental changes effectively. Understanding these levels is fundamental for studying anatomy and physiology.
4.2 Body Systems and Their Functions
The human body comprises 11 major systems, each with distinct functions. The nervous system controls communication, the circulatory system transports blood, and the respiratory system facilitates breathing. The digestive system processes nutrients, while the urinary system filters waste. The endocrine system regulates hormones, and the integumentary system protects the body. Muscular and skeletal systems enable movement, and the immune system defends against pathogens. Reproductive systems support reproduction, while the lymphatic system aids immunity. Together, these systems maintain homeostasis and overall health.

Anatomical Terminology
Anatomical terminology is the language of healthcare, essential for precise communication. It includes positional terms (e.g., superior, inferior) and directional terms (e.g., anterior, posterior) to describe body positions and movements accurately.
5.1 Positional Terms
Positional terms describe the location of body parts relative to each other. Superior refers to a structure above another, while inferior is below. Anterior is toward the front, and posterior toward the back. Medial indicates near the midline, while lateral is away from it. Proximal is closer to the body’s center, and distal is farther away. These terms provide a standardized way to communicate anatomical locations, ensuring clarity in healthcare and scientific discussions. Mastering them is essential for accurate descriptions and understanding of bodily structures and their relationships.
5.2 Directional Terms
Directional terms define the orientation of body parts. Anterior refers to the front, while posterior is the back. Dorsal is toward the upper surface, and ventral toward the lower. Rostral indicates toward the head, and caudal toward the tail. These terms help describe movement and location in precise anatomical language. They are essential for clear communication in healthcare, ensuring accuracy in descriptions of body orientation and spatial relationships. Understanding directional terms enhances the study of anatomy and physiology, aiding in diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
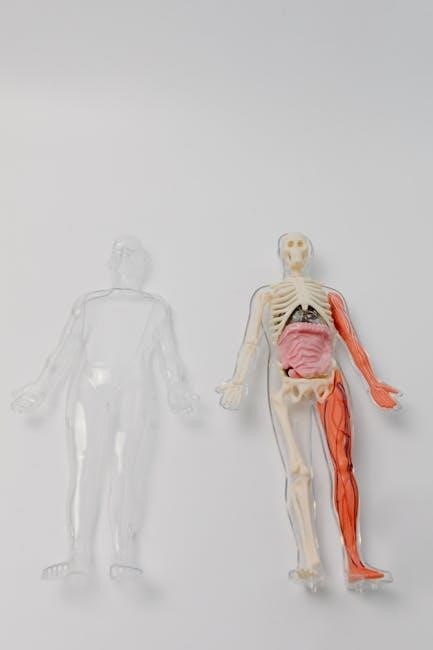
Physiology of Major Body Systems
Physiology of major body systems explores how the nervous, circulatory, and respiratory systems function. These systems work together to maintain homeostasis and ensure overall health. Understanding their interconnected roles is crucial for advancing medical knowledge and treatments.
6.1 Nervous System
The nervous system is a complex network controlling voluntary and involuntary body functions. It consists of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system. Neurons transmit signals, enabling communication between different body parts. The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary actions like heart rate and digestion. Understanding nervous system physiology is crucial for diagnosing neurological disorders and developing treatments. It highlights how the body responds to stimuli and maintains homeostasis, essential for overall health and function.
6.2 Circulatory System
The circulatory system, also known as the cardiovascular system, transports oxygen, nutrients, and hormones throughout the body while removing waste products. It consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart acts as a pump, propelling blood through arteries, veins, and capillaries. This system supports immune function, regulates body temperature, and maintains homeostasis. Understanding its physiology is vital for addressing conditions like hypertension, atherosclerosis, and heart failure, which are common in clinical practice and require precise anatomical and functional knowledge for effective treatment;
6.3 Respiratory System
The respiratory system facilitates gas exchange, bringing oxygen into the body and expelling carbon dioxide. It includes the nose, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. Inhalation and exhalation are regulated by the diaphragm and intercostal muscles. Oxygen diffuses into the bloodstream through alveoli in the lungs, while carbon dioxide is removed. This system is vital for cellular respiration and maintaining acid-base balance. Understanding its anatomy and physiology is crucial for managing conditions like asthma, COPD, and pneumonia, which impact breathing and gas exchange efficiency.

Study Resources and Notes
Comprehensive anatomy and physiology study notes and guides are widely available, offering detailed insights into body systems, functions, and key concepts. High-yield notes and PDF resources provide structured learning materials, ideal for exam preparation and in-depth understanding of complex topics.
7.1 Best Anatomy and Physiology Study Guides
Premium anatomy and physiology study guides offer comprehensive, well-structured materials, including detailed notes, diagrams, and practice questions. Many guides are available in PDF format, providing easy access and portability. They cover essential topics like body systems, cellular structure, and physiological processes. High-yield notes and summaries are particularly useful for exam preparation, ensuring students grasp key concepts efficiently. These guides often include visual aids, making complex topics more understandable and engaging for learners at all levels.
7.2 High-Yield Anatomy and Physiology Notes
High-yield anatomy and physiology notes are concise, focused study materials that prioritize essential concepts and information. These notes are designed to help students quickly grasp key topics, making them ideal for exam preparation. Organized by body systems, they often include detailed diagrams, summaries of physiological processes, and key terminology. Available in PDF format, they provide a structured approach to learning, ensuring efficient retention of critical information. These notes are particularly valuable for medical and healthcare students seeking to master complex subjects effectively.
7.3 Free PDF Resources for Anatomy and Physiology
Free PDF resources for anatomy and physiology are widely available online, offering comprehensive study materials for students. These resources often include detailed notes, diagrams, and summaries of key concepts. Platforms like educational websites and forums provide downloadable guides covering topics such as body systems, cellular structure, and physiological processes. Many resources are organized by chapters or systems, making it easier to focus on specific areas of study. These free PDFs are invaluable for supplementing textbooks and lecture materials, ensuring accessible learning for all students.
Tips for Effective Study
Active learning, using visual aids, and regular review are key to mastering anatomy and physiology. Engage with diagrams, flashcards, and practice questions to enhance retention and understanding.
8.1 How to Prepare for Anatomy and Physiology Exams
To excel in anatomy and physiology exams, organize your study materials, including high-yield notes and free PDF resources. Focus on understanding key concepts rather than memorizing details. Use flashcards to review anatomical terms and physiological processes. Practice labeling diagrams and answering case-based questions. Regularly test yourself with practice exams to identify weak areas. Utilize visual aids like charts and videos to reinforce learning. Review lecture notes and textbook summaries consistently, ensuring mastery of foundational topics before moving to advanced ones. Seek clarification on complex subjects from instructors or study groups. Stay organized and create a study schedule to cover all topics thoroughly. Prioritize active learning techniques, such as teaching the material to others or engaging in group discussions, to enhance retention. Incorporate real-world applications to make studying more engaging and relevant. Regular breaks and a well-balanced study routine will help maintain focus and reduce exam stress. By combining these strategies, you can achieve a deep understanding of anatomy and physiology, leading to success in your exams.
8.2 Using Visual Aids for Better Understanding
Visual aids like diagrams, charts, and 3D models are essential for mastering anatomy and physiology. They help students visualize complex structures and processes, enhancing retention. Use high-yield PDF notes with labeled illustrations to study body systems. Videos and animations can demonstrate physiological processes, such as blood circulation or nerve impulses. Flashcards with images are also effective for memorizing anatomical terms. Incorporate these tools into your study routine to deepen your understanding and improve exam performance. Visual learning simplifies complex concepts, making them easier to grasp and apply.
Applications in Healthcare
Anatomy and physiology are vital in healthcare for disease diagnosis, treatment development, and patient care. They guide surgeons, nurses, and therapists in precise interventions and rehabilitation strategies.
9.1 Clinical Relevance of Anatomy and Physiology
The clinical relevance of anatomy and physiology is profound, enabling healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat conditions accurately. Understanding body structures and their functions aids in identifying abnormalities, guiding surgical interventions, and developing personalized treatment plans. For instance, knowledge of organ systems helps in pinpointing disease origins, while physiological processes inform drug therapies and rehabilitation strategies. This foundation is essential for effective patient care and advances in medical research.
9.2 Advances in Medical Research
Advances in medical research heavily rely on anatomy and physiology, providing insights into organ functions, disease mechanisms, and treatment development. These studies enable breakthroughs in regenerative medicine, tissue engineering, and personalized therapies. Understanding physiological processes aids in developing drugs and surgical techniques, improving patient outcomes. Research in anatomy and physiology also drives innovations in diagnostic imaging and prosthetics, enhancing healthcare delivery. Continuous exploration of these fields ensures ongoing progress in addressing complex medical challenges and improving human health;

